Best 3D Printing Software
Best 3d printing software are Meshlabs, Catia, Scupteo, and OnShape. Best 3D printing software will help you understand and design different types of 3D shapes in real-time



No Cost Personal Advisor
List of 20 Best 3D Printing Software
Contenders | 2024
Software by Ultimaker BV
Cura is an effective and user-friendly 3D printing slicing program that enables users to slice and prepare 3D models for printing as well as configure and optimize print parameters for various 3D printers and material combinations. It is 3d printing design software that UltiMaker created and maintained for free download. Read Ultimaker Cura Reviews
Explore various Ultimaker Cura features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all Ultimaker Cura Features- For 3D Printing
- 3D Modeling
Ultimaker Cura Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Autodesk Inc.
A collection of online Autodesk software tools called Tinkercad enables even total beginners to create 3D models. This CAD program's and 3d printer's foundation, constructive solid geometry (CSG), enables users to mix more basic components to create more sophisticated models. It is one of the best 3d printer design software, which is widely used. Read Tinkercad Reviews
Explore various Tinkercad features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Tinkercad Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by FreeCAD
FreeCAD is a multi-purpose finite element method-compatible building information modelling and parametric 3D computer-aided design modeller. FreeCAD is one of the best modeling software for 3d printing. You can use the 2D forms you develop with FreeCAD as a starting point that can aid you in designing other items. It has numerous components that can be used to change measurements or extract design information from 3D models to produce drawings that are excellent enough for production. Learn more about FreeCAD
Explore various FreeCAD features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all FreeCAD Features- Annotations
- For Architects
- Data Import / Export
- Simulation
- For Manufacturers
FreeCAD Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by RS Components
DesignSpark Mechanical is popular free 3D CAD solid modelling software. Users can create solid models in a 3D environment and produce files for 3D printers using DesignSpark Mechanical. It permits limitless and frequent design changes by employing the direct modelling technique and a user-friendly collection of tools. Learn more about DesignSpark Mechanical
Explore various DesignSpark Mechanical features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
- Data Import / Export
- Bill of Materials
- Annotations
- 2D Drawing
- For 3D Printing
- Component Library
- For Manufacturers
DesignSpark Mechanical Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Contenders | 2024
Software by Blender
Blender is an open-source and free 3D creation tool. This is one of the best programs for 3d printing, which supports simulation, rendering, rigging, animation, Modelling, compositing, game development, motion tracking, and even video editing. Python is a language for creating visual scripts that are used to power all of Blender's features. Read Blender Reviews
Explore various Blender features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Blender Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Contenders | 2024
Software by Autodesk Inc.
You can design in 3D, collaborate, make toolpaths, manage data, and test your designs by utilizing simulations with Fusion 360, one of the best 3d printing software. Experts in manufacturing, engineering, machining, and industrial design also regularly use Fusion 360 as their tool of choice. Users can complete a large portion of the design workflow with the software without ever having to switch programs. Read Fusion 360 Reviews
Explore various Fusion 360 features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all Fusion 360 Features- For Architects
- Project Management
- Rules-Based Workflow
- Database Connectivity
- Design Templates
- Collaboration
- Text Editing
- Version Control
Fusion 360 Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Onshape Inc.
Multiple people can access and work on a single design simultaneously over the cloud using any tablet, computer, or phone, thanks to the Onshape CAD system. Similar to how multiple authors can collaborate on updating a shared text using cloud services, Onshape is a 3d printing software that enables teams to work together on a single shared design. Learn more about Onshape
Explore various Onshape features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Pricing
Education
$ 0
Per Month
Public
$ 0
Per Month
Professional
$ 125
Per Month
Onshape Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Autodesk Inc.
An excellent free program for producing and modifying 3D files for 3D printing is Meshmixer. This is one of the best modeling software for 3d printing, which can be used to design objects, clean up 3D scans, or even perform some 3D printing. With the aid of the tools provided by Meshmixer, you may transform your current CAD drawings into parts that are suitable for 3D printing. Learn more about Meshmixer
Explore various Meshmixer features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Meshmixer Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Best-in-Class 3D Print Management System
The slicing tool Simplify3D converts a 3D model into a g-code file that a 3D printer can read and comprehend. In ways that its rivals can't match, Simplify3D offers total control over the 3D printing process. Your 3D printer's possibilities are expanded by customizable support structures, changeable part settings, focused customizations, and a distinctive process system with this 3d printer program. Learn more about Simplify3D
Explore various Simplify3D features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Pricing
Starter
$ 149
Per Month
Simplify3D Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Sculpteo
Sculpteo is a renowned 3d printing software. The business offers 3D printing services online and the creation of products from 3D files for consumers, companies, and manufacturers. The client can upload his 3D model to the website and instantly receive an estimate. Thanks to several production technologies such as stereolithography, selective laser sintering, HP Multi Jet Fusion, FDM, etc., Sculpteo provides a rapid prototype service, manufacture on demand, or contract manufacturing. Learn more about Sculpteo
Explore various Sculpteo features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Sculpteo Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Slic3r
Handle 3D models and get access to a visual preview of toolpaths by using Slic3r, the open-source 3d printing solution. Build custom applications, generate G-code or export SVG slices; this software is a handy tool for professionals. Learn more about Slic3r
Explore various Slic3r features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Slic3r Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Contenders | 2024
Software by SolidWorks Corporation
The entire process of creating mechatronic systems can be easily undertaken using the 3d printer program SolidWorks. The software is initially used for planning, project management, modelling, visual ideation, feasibility analysis, and prototyping. Following that, the program is used to design and build mechanical, electrical, and software components. Read SolidWorks Reviews
Explore various SolidWorks features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all SolidWorks Features- 2D Drawing
- Collaboration
- Custom Pricing Options
- For 3D Printing
- Analysis & Constraints
- 3D Modeling
- Data Import / Export
SolidWorks Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Robert McNeel & Associates
Working with curves or mathematical formulas that precisely describe a 3D geometry is possible with one of the best 3d printer design software, Rhino 6. This surface modelling program is frequently used in the design of industrial, graphic, nautical, and automotive structures and prototypes. Rhinoceros 3D is a CAD program with numerous sophisticated 3D modelling capabilities that let you accurately and precisely design unfathomable shapes from sketches, drawings, or even 3D scans. Learn more about Rhino 6
Explore various Rhino 6 features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all Rhino 6 Features- Fashion Illustrations
- Presentation Tools
- Design Export
- 2D Drawing
Rhino 6 Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Pixologic
From customizable brushes, real-time environment for sculpting and painting to advanced designing features, Zbrush is a reliable 3D printing tool. Whether you are a gaming enthusiast or working with a film studio, give an edge to your artistic skills with this art tool. Drive your imagination at a high pace as Zbrush offers improved base mesh generation quality for printing. Learn more about Zbrush
Explore various Zbrush features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Pricing
Single User Monthly Subscription
$ 40
Per Month
Single User 6 Month Subscription
$ 180
Per 6 Month
Single User Perpetual License
$ 895
One Time
Zbrush Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Easy to use online 3D modeling software.
Using SelfCAD, you may create 3D designs, models, sculptures, sketches, renders, and animations. SelfCAD is a browser-based, online CAD/CAM tool that enables online modelling, slicing, sculpture, as well as printing. It is one of the best programs for 3d printing. Once loaded, it can function flawlessly offline. Read SelfCAD Reviews
Explore various SelfCAD features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all SelfCAD Features- Data Import / Export
- Animation
- For Manufacturers
- 3D Modeling
- For 3D Printing
Pricing
Monthly Plan
$ 5
Per Month
Yearly Plan
$ 40
Per Year
SelfCAD Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Mixed Dimensions
A cloud-based service called MakePrintable evaluates and fixes any 3D model for 3D printing. It is a Mixed Dimensions creation. At MakePrintable, the 3d printing design software, the goal is to make the transition from 3D content to 3D printing as seamless as possible. The tool assures print success, making it easier for anyone to begin 3D printing. Learn more about MakePrintable
Explore various MakePrintable features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all MakePrintable Features- Data Import / Export
- Animation
- Project Management
- 3-Axis Milling
- Document Management
- Design Templates
- Archiving & Retention
- Drag & Drop
MakePrintable Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Designing software for solid 3D CAD objects
A free program called OpenSCAD can be used to build 3D solid computer-aided design objects. OpenSCAD is one of the best 3d printer programs, which is a descriptive, text-based programming language that combines basic geometric primitives into more complicated objects using a well-known syntax, if statements, for loops, variables, and arithmetic. Learn more about OpenSCAD
Explore various OpenSCAD features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all OpenSCAD Features- Collaboration
- Symbol Library
- Drag & Drop
- Document Generation
- Functions / Calculations
- Reusable Designs
- One Line Diagram
OpenSCAD Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Emergents | 2024
Software by Meshlab
MeshLab is an open-source program used to edit and process 3D triangular meshes. This 3d printer modeling software offers a set of tools for editing, rendering, cleaning, inspecting, healing, and converting a wide range of meshes. The administration and processing of large, unstructured meshes is the primary emphasis of this 3D mesh processing software system. Learn more about Meshlab
Explore various Meshlab features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Meshlab Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Contenders | 2024
Software by Autodesk Inc.
The Autodesk product AutoCAD Electrical was created specifically for electrical, instrumentation, and control system designers, and it aids in the creation and modification of electrical control systems. Because this 3d printer program is the most dependable and has toolsets unique to the industry that are useful for developing motor components, engines, and full devices, AutoCAD is a popular CAD program used by engineers. Read AutoCAD Electrical Reviews
Explore various AutoCAD Electrical features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
AutoCAD Electrical Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises
Contenders | 2024
Software by Brandvee
Maya is a set of professional 3D animation, rendering tools and modelling made for producing realism in characters and effects that are suitable for a Hollywood blockbuster. This is one of the best 3d printing software. Top artists, modellers, and animators rely on Maya's award-winning toolbox to make the animated and live-action films, video games, TV shows, imaginative animals and massive landscapes. Read Maya Reviews
Explore various Maya features, compare the pricing plans, and unlock the potential of seamless operations by selecting the right software for your business.
Features
View all Maya Features- Editorial Calendar
- Distribution Management
- Audience Targeting
- Conversion Tracking
- Publish Scheduling
Maya Caters to
- StartUps
- SMBs
- Agencies
- Enterprises

What is 3D Printing Software?
Every 3D print begins as a 3D model generated with the help of modeling programs. These modeling programs are browser-based 3D design applications. The software is like a building block for users who want to develop 3D models using basic shapes. It lets users access the library of millions of shapes and finds shapes that suit them to further manipulate it.
3D printing is sometimes also referred to as additive manufacturing. The software offers feature-rich tools for sculpting, rendering, video editing, animation, simulation, and motion tracking. 3D printing software encompasses a wide variety of products such as slicers, computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), computer-aided design (CAD), design automation, and others.
CAD covers the part where designing, scaling, and features take part, along with a few CAD software such as Autodesk Inventor, Siemens NX, etc. The result of this phase would fetch a 3D digital model. In comparison, CAM takes care of the preparation and manufacturing process. The result of this phase would fetch the real 3D object.
The best 3D printing software should be able to deliver the following things:
- Flexibility for a variety of workflows
- A reliable process that delivers accurate results with minimal configuration
- Optimization of print duration, part strength, and material used
- Support for multi extrusion printers
- Functional scalability
Role of software in 3D printing workflow no matter what 3D printer user may use is an essential step is preparing a 3D model file first using slicing software (also called slicer). The basic function of the slicer is to slice the 3D file into horizontal layers to make it suitable for the further printing process. Besides this, a slicer can be considered a toolkit capable of performing complex functions to prepare a 3D model for fabrication.
Why Use 3D Printing Software?
Here are the top benefits of the best 3D printing software that customers must keep in mind while buying it:
-
Less Turnaround Time
Rapid prototyping is the primary benefit of 3D printing software. It enables companies to meet consumer demands in less time. With rapid prototyping, it becomes possible to test the designs created through CAD software and eliminate the errors without actual loss. This takes not more than a couple of days. However, the traditional method takes a couple of weeks.
-
Cost Saving
3D printing is the most cost-effective process. It does not require costly custom-made tools and equipment its working. Companies can easily replace the 3D printing tools without wasting much time and cost.
-
Freedom in Designing
With 3D printing, it becomes possible to create complex geometry easily. This will let you simplify your designs and add more creativity to them. This easy-to-use tool can be used by anyone, even with less experience in CAD. You can create and customize unique designs as per your requirement.
-
Reduced Waste
3D printing uses only the required amount of material for the manufacturing process. Unlike the traditional methods that use large amounts of materials and cut away the major portion of it as waste during the actual process. The 3D printing process reduces waste and saves on the cost of the material.
-
Competitive Advantage
With very less manufacturer to consumer time, 3D printing offers a competitive advantage to the companies. The companies enhance their product and make changes in the product based on the feedback collected from the potential customers. This lets them in saving the time required for future changes in products and cuts down the waste.
-
High Quality and Consistency
3D printing gives high-quality products to companies with its step-by-step designing method. This shows the designers how the 3D printing process is progressing and lets them make changes at that particular step itself. Traditional methods, on the other hand, may result in low-quality designs and poor prototypes.
In manufacturing processes, usually, a bunch of products is manufactured at a time. With the traditional method, there are high chances that the products manufactured can turn defective and inconsistent simultaneously. 3D printing solves this problem. Here parts are manufactured in series and are monitored such that all the errors are eliminated, thereby increasing the consistency of the process.
-
Great Accessibility and Environment Friendly
3D printing does not require high skills and huge experience. Hence, it can be used by a broader range of individuals. Implementing this process is quite easy and cost-friendly. Thus, smaller organizations can also implement it. It becomes more accessible with the automation in its process and requires less monitoring.
3D printing has a low impact on the environment as it does not require high-level energy consumption. It also creates minimal waste, and the best part is the materials are mostly recyclable.
What are The Features of 3D Printing Software?
Let's look at the features and attributes of 3d printing software:
-
Printing Materials
The fast and efficient 3D printing software uses various materials for 3D printing. These materials come in different temperature ranges. Different materials include nylon, polycarbonate, PVA, PLA, and the list continues.
-
Integration
The base of a 3D print job is formed of 3D models. 3D printers should be able to communicate with these tools so that data from a 3D modeling software can be accessed and converted into a form that the 3D printer recognizes.
-
Printer Support
3D printing tools should have good compatibility with the range of 3D printers. It is especially important to make sure that the 3D printing software you choose is compatible with the 3D printer you will be using.
-
Designing Tools
The designing tools comprise drawing tools, 3D modeling, visualizing, rendering, and editing tools. With these tools, you can edit the design using 3D printing software.
-
Software Type
This feature gives you the option of software type. The 3D printing software comes in two software types: either you can opt for a cloud-based platform or you can download the application and make the best use of it.
-
Preprint Issue Identification
By running a preprint model, you can get information, including real speeds and series. This ensures you go ahead with the print job only when you are certain that it will be satisfactory.
-
Adjustable Print Settings
With the 3D printing software, you can get variable print settings that can be used for distinct sections of your print. This simple-to-understand setting can be done with a couple of clicks on the software.
-
Compatibility with Machines
Software that is involved in manufacturing execution must be able to integrate with machines easily. The large quantity of data must be easily transferred.
-
Fabrication Process & Mending Services
In the fabrication process, the CAD file is converted into an STL file for the final printing of the object. These files are further handled by slicer software, where users can also configure the software to support a few actions such as overhangs and supports (needed in FFF printing).
Sometimes the STL could be poorly exported, leading to unnecessary troubles. Hence, to avoid this, there must be some backup tools that rectify the problems.
-
Customizable
The software must be able to adapt and meet unique cultural/language requirements depending upon the need of users and their workflow.
-
Planning, Scheduling, & KPI Dashboards
Planning & scheduling is an important part of any job; hence 3D printing also plays an important role. For any workflow to be smooth, users must be able to plan and schedule their actions. Along with this, users must also be able to keep an eye on the activity. The KPI Dashboard lets the user be more productive by sharing a report of their activities. Data has become the heart of any process; hence software must be able to perform analysis for better productivity.
-
Communication
While working on a large scale, proper team communication is required; it helps keep everyone connected. The 3D printing software eliminates the part where everyone had to be informed manually by sending mails. Now teammates are notified through the software.
Not only teammates but clients are also involved as they need updates too; hence it is expected that the software facilitates communication with ease. As 3D printing software offers a centralized platform, maintaining clients and team communication logs are easily handled.
-
Avoiding Distortion
Software must be able to indicate early in the process about possible distortions. It should be able to anticipate distortion and fix the geometry of the object before the actual printing takes place.
If the 3D printing software includes the above-mentioned attributes, it will fetch you ideal results. Talking about attributes, here is a list of things you can expect to be trending in 3D printing and related to 3D printing in the upcoming years.
What are The Types of 3D Printing Software?
There are various 3D printing solutions developed to build real-life 3D structures and objects. All 3D printing systems have the same result. However, some 3D printing software solutions are prevalent nowadays, and others have fallen by the wayside due to changes in how they print out objects. Below find a list of the most common 3D printer tool used in 3D printing today - stereolithography (SLA), fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering (SLS), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), polyjet or multijet printing (MJP), Inkjet printing, electron beam melting (EBM), laser metal deposition (LMD), laminated object manufacturing (LOM), and digital light processing (DLP). DMLS, SLS, and FDM are the most established and the best 3D printing software widely used in 3D printing technology.
-
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
DMLS is also called direct metal laser melting (DMLM). This method is similar to that of the SLS-based 3D printers; the only difference lies in the materials used. DMLS is used for building metal parts, and SLS is used for printing plastic-based parts. DMLS is used for rapid prototyping and mass production of metal parts such as Inconel, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. DMLS-based 3D printing solution is ideal for developing oil and gas components, custom medical guides, consolidated aerospace parts, and difficult functional prototypes.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS is a new technology mainly used for rapid prototyping and low-volume production of component parts. The SLS-based 3D printer uses a high-power laser source to sinter small particles of polymer powdered material (nylon or polyamide) to create a solid structure. The common material used for the SLS process is nylon, a lightweight, strong, and flexible engineering thermoplastic that has excellent mechanical properties.
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused deposition modeling is also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), Plastic jet printing (PJP), or filament freeform fabrication. FDM is the most common and widely used printing solution at the consumer level. FDM 3D printing process uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material.
-
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is also known as stereolithography apparatus, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing. Stereolithography is the oldest, most popular, and best 3D printing software used by professionals. SLA uses lasers and mirrors to print out an object layer by layer. SLA 3D printing technology is used for lightweight concept models, prototypes, anatomical models, form and fit studies, architectural models, urethane casting patterns, investment casting patterns, and production parts, as this technology provides a high-quality surface finish.
SLA resin 3D printers could deliver accurate, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and parts with fine features and a smooth surface finish. This is a particularly good option for highly detailed prototypes that needs tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. SLA resin formulation offers a broad range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties to suit those of standard, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
The major companies offering SLA-based 3D printers and services are 3D Systems, Form Labs, Autodesk, and 3D Ceram. SLA-based 3D printer systems are widely used in engineering, product design, short-run manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry prototyping and casting, model making, and education industries.
What are The Common 3D Printing Problems and Solutions?
-
3D Design
Since the 3D industry is evolving rapidly now and then, new kinds of materials are introduced in the industry, but the user needs to understand what kind of material will suit them the best. As 3D printing goals are different, one must know if they want solid or flexible output. Now, based on these goals, one needs to correctly choose their 3D design, or the output can be of totally different quality. Hence, it is suggested to carefully choose the right material and follow design guidelines as it will save a lot of money and time.
-
3D Printing String
This is one of the most common problems faced by people using 3D printers. In this case, the melted plastic oozes out of the nozzle while printing the object. The oozed-out plastic solidifies, and it is difficult to get rid of it. Users can overcome this problem by enabling retraction. When we do this, the filament inside the nozzle is pulled back and stopped from moving. Also, increasing the retraction speed will decrease the chances of stringing.
-
3D Print Wrapping:
This occurs when deposited material starts cooling during the printing process. Such untimely and uneven cooling causes the parts to deform, resulting in a defective object as output. To avoid this issue, heated print beds are used, due to which the time increases for the layers to cool down when it is deposited, saving filaments from wrapping. Another idea is to build surface adhesion; it will help with other filaments.
-
3D Print Pillowing:
This occurs on the object that is printed with a 3D printer. The object has holes and deformities formed on its topmost layer. This occurs due to improper cooling as the top layer fails to get enough cool air. To overcome this, one must set a thick topmost layer and adjust cooling.
Top 5 3D Printing Software For Beginners
|
Name
|
Free Trial
|
Demo
|
Pricing
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Free |
Yes |
Free | |
|
14 Days |
Yes |
Starting price at $2/month |
|
|
Free |
Yes |
Free |
|
|
Free |
Yes |
Free |
|
|
Free |
Yes |
Free |
3D printing opens a world of creativity, and selecting the right software is crucial. Our carefully curated list showcases user-friendly options, empowering beginners to dive into the fascinating realm of 3D printing. Whether you're a hobbyist or an aspiring designer, these best software for 3D printing offer intuitive interfaces and essential features to bring your imagination to life. Let's get started with the best 3D printing software for beginners!
1. TinkerCAD
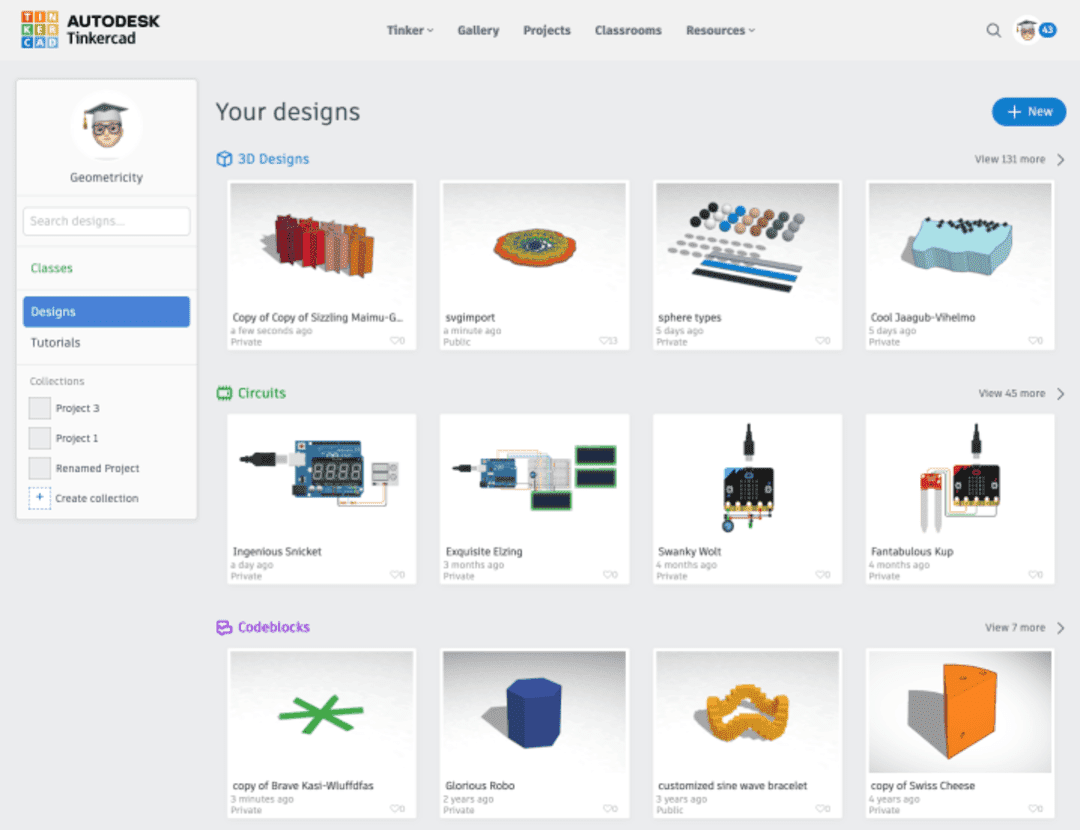
Tinkercad is a beginner-friendly 3D design software establishment that allows users to create complex models using an intuitive and easy-to-use interface. The 3D printing software for beginners includes various shapes and tools that can be used to design intricate models with ease. Hence, making it an excellent option for beginners looking to get into 3D printing. Additionally, Tinkercad offers a vast library of ready-to-use models, making it an excellent resource for individuals who want to get started with 3D printing but are unsure where to begin.
- Add pre-existing basic shapes
- Create custom shapes
- Preview and align multiple objects along any axis
- Create exact duplicates of stl files
- Turn designs into augmented reality (AR)
- The fundamental elements of Tinkercad are free, so users may design and make 3D models without having to purchase pricey software
- The platform's user interface is clear and simple to use, making it a fantastic choice for newcomers to the field of 3D modeling
- Shape generators, modeling tools, and object grouping are just a few of the fundamental capabilities that users of the free cad software will require for 3D design
- Due to the ease with which users may share their designs with others on an internet platform, it's excellent for educational uses, such as for school assignments
- While Tinkercad may be excellent for novices, it falls short of more sophisticated software packages in terms of design skills, making it unsuitable for more difficult tasks
- Tinkercad may not be appropriate for professional 3D design work due to its limited functionality, especially when compared to other software solutions available on the market
- The platform's fundamental capabilities are simple to use, but more experienced users may discover that they restrict their creativity, for example, by preventing them from merging objects or creating new forms
Pricing
- It is free.
2. 3D Slash
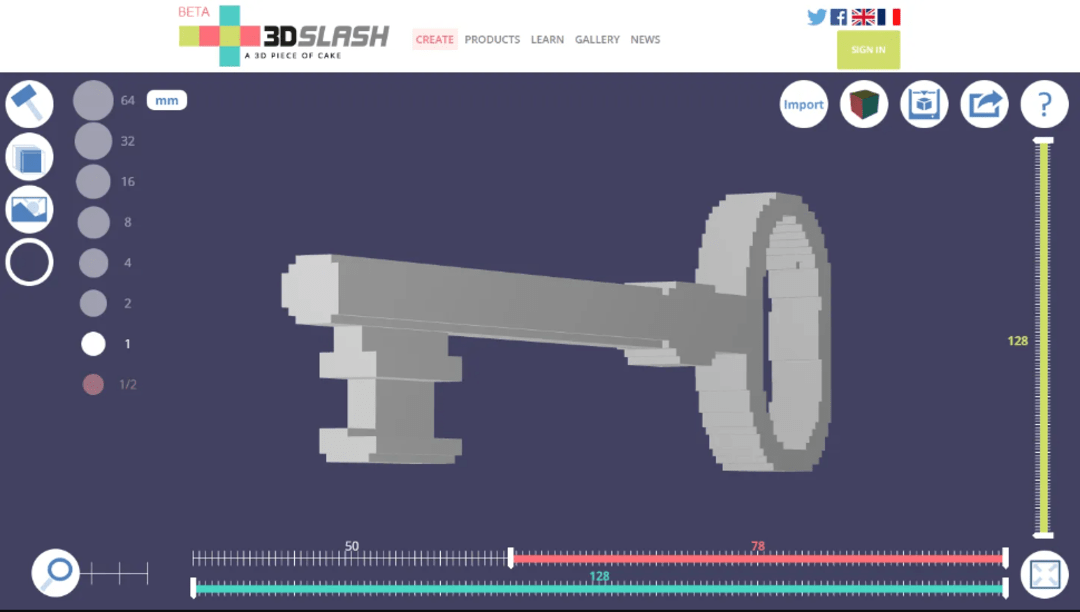
3D Slash is a unique and innovative 3D printer design software that utilizes a block-based modeling system. The software employs a drag-and-drop interface and simple commands to create complex 3D models quickly and easily, making it an excellent option for beginners. Additionally, this web-based open-source slicer software can be used on any device with an internet connection. Hence, allowing users to work on their projects from anywhere.
- Stl file or .obj file, or g code file startup
- High precision modelling
- Image and photographic sculpt shapes
- Very light files
- Insert rounded shapes
- 3D Slash boasts a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to beginners without prior 3D modeling knowledge
- No downloads or plug-ins are required as the platform operates solely online, perfect for users with limited storage space
- The software allows users to import personal photos and use them to create new 3D models or modify existing ones, offering great design flexibility
- Its basic version is free, with reasonably priced paid options, making it cost-effective for budget-conscious designers
- Due to its basic nature, 3D Slash lacks some advanced features found in other 3D modeling programs, limiting design control for some users
- While the software is easy to use, mastering specific tools may take time, especially for those new to 3D modeling
- Compared to more popular 3D modeling systems, 3D Slash has a smaller user base, potentially making it harder to find support and information
Pricing
- Free
- Premium- $2 per month
- Schools- $12 per month
- Professionals- $20 per month
3. Meshmixer
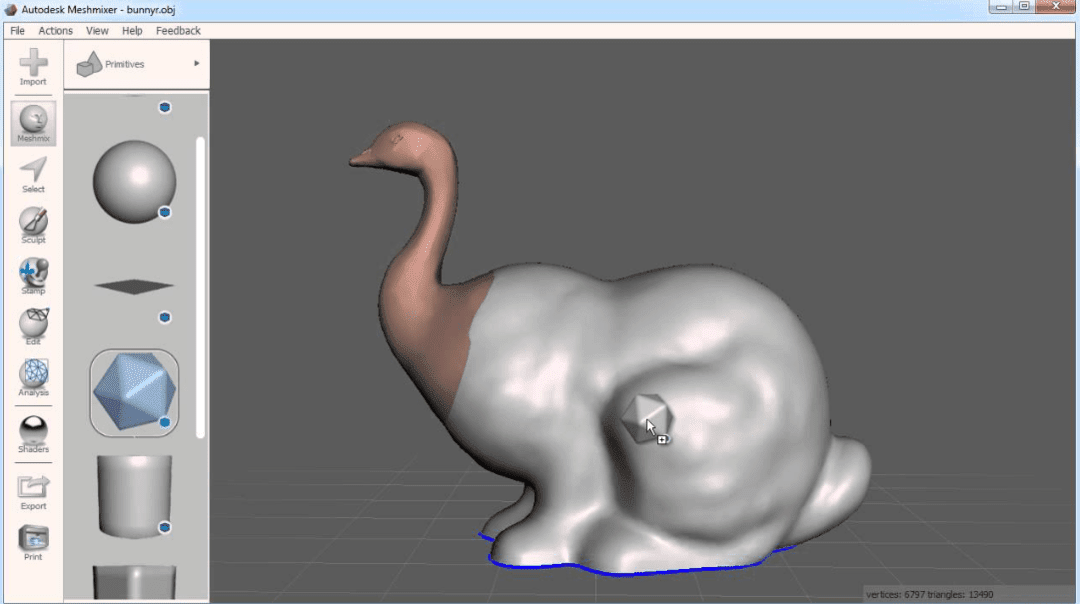
Meshmixer is one of the best software for 3D printing tailored for artists, engineers, and makers seeking to craft captivating models effortlessly. Its intuitive interface and powerful mesh editing tools make it a top choice for both novices and experts. By offering an array of base models and versatile sculpting brushes, this platform fosters a creative environment for crafting visually appealing 3D designs. Available for Windows and Mac OS, Meshmixer is a free download, enhancing accessibility for all users.
- Drag-and-drop mesh mixing
- 3D sculpting and surface stamping
- Robust convert-to-solid for 3D printing
- Remeshing and mesh simplification/reducing
- Mesh smoothing and free-form deformations
- Meshmixer offers a simple and user-friendly interface, making it accessible and easy for beginners to grasp quickly
- Professionals benefit from its advanced features like sculpting, mesh analysis, and 3D printing support, catering to their specific needs
- As open-source software, Meshmixer is free to use and allows developers to customize it for their unique requirements
- Its versatility enables users to create 3D models for various applications, including gaming, animation, and engineering
- Beginners may find it challenging to learn due to the software's advanced capabilities
- Meshmixer supports only a limited number of file formats, restricting users who work with other 3D models
- The absence of a large online support community makes it harder to access helpful resources when needed
Pricing
- It is free.
4. Ultimaker cura
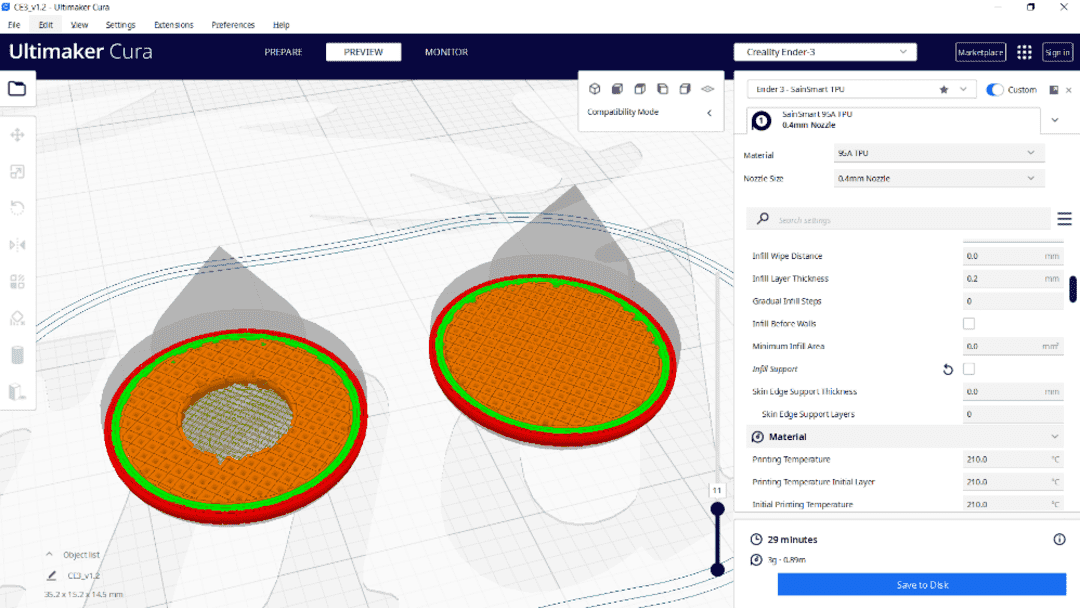
Ultimaker Cura stands out as a widely favored free and open-source 3D printing software, drawing praise from novices and experts alike. Its user-friendly interface makes it accessible for all, offering a plethora of customization options and advanced features that guarantee top-notch 3D prints. The software's versatility is evident in its compatibility with a diverse range of 3D printers. Additionally, the active user community fosters collaboration, while frequent updates keep it at the forefront of technology.
- Single click print specific applications
- Meticulous profiles testing
- Over 400 settings for granular control
- Compatible file types: STL, OBJ, X3D, 3MF, BMP, GIF, JPG, PNG
- Users can simply operate Ultimaker Cura thanks to its user-friendly UI
- The software enables users to produce accurate and detailed 3D prints that are of a high grade
- The software gives users complete control over the printing process by providing a wide range of customization choices, including speed, layer height, and support structures
- As open-source software that is free to use, Cura is available to all users
- Ultimaker Cura is regularly updated with fresh functions and enhancements, giving consumers access to dependable and current software
- Because of the software's high computing requirements, users with less powerful computers may find it difficult to use it
- Cura's interoperability with other printer brands and models is constrained because it is primarily made to work with Ultimaker 3D printers
- Because of the software's numerous customization possibilities, users must take the necessary time to become familiar with all of its capabilities and adjust their print settings
- Like every software, Cura occasionally has issues or malfunctions, which can be annoying for users who need to finish projects right away
Pricing
- It is free.
5. MeshLab
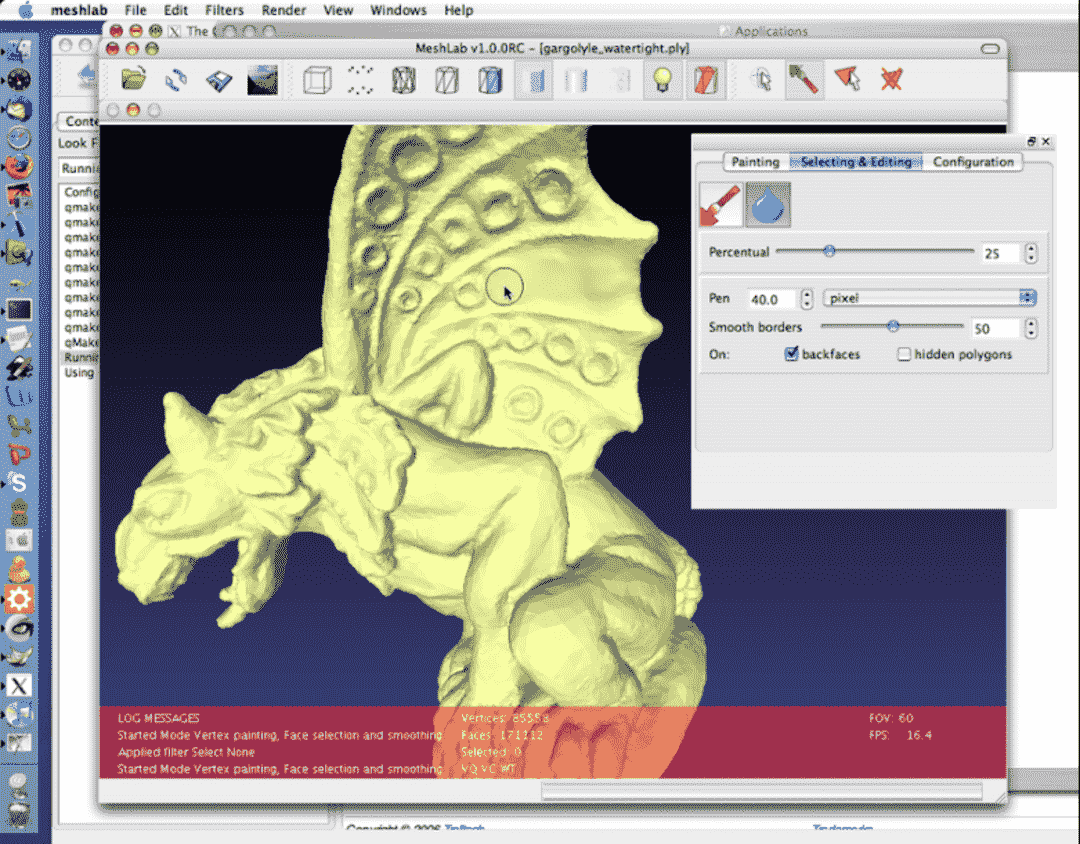
MeshLab, an open-source 3D editing software, empowers artists, designers, and hobbyists with its user-friendly interface and robust tools for creating, editing and manipulating 3D meshes. From character sculpting to architectural design or data exploration, MeshLab offers the flexibility and power to bring your ideas to life effortlessly. It's the ideal choice for unleashing your creativity and realizing intricate projects.
- Visualization and presentation
- Color processing
- Color mapping and texturing
- Offsetting, hollowing, closing
- 3D models conversion and interchange
- MeshLab supports various 3D file formats, like PLY, STL, OBJ, 3DS, VRML, and more, enhancing versatility
- The software's customizable interface caters to different user needs and preferences
- With a plethora of tools, MeshLab excels in processing, editing, measuring, and analyzing 3D models
- Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, it offers flexibility for diverse user platforms
- As open-source software, MeshLab is free to use, modify, and distribute, facilitating personalized customization
- Beginners, especially those new to 3D modeling, may find MeshLab's complexity challenging to learn
- Users might experience occasional glitches and technical issues, causing frustration
- The limited support community might necessitate self-help for troubleshooting problems
Pricing
- It is free.
Best 3D Printing Software for Experts
|
Name
|
Free Trial
|
Demo
|
Pricing
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
30 Days |
Yes |
Starting price at $56.95/month | |
|
30 Days |
Yes |
Starting price at $187.91/month |
|
|
90 Days |
Yes |
Commercial for Windows and Mac US$ 995 |
|
|
30 Days |
Yes |
Starting price at $9.91/month |
|
|
30 Days |
Yes |
Custom pricing |
In this comprehensive section below, we present the Best 3D Printing software for experts. Designed to elevate your 3D printing game, this software caters to the needs of seasoned professionals. Thus, offering advanced features, intricate controls, and unparalleled precision. Discover the best design software for 3D printing to unleash your creativity and achieve exceptional results. Let's see the 5 best 3D software for 3D printing for experts in detail:-
1. Autodesk fusion 360
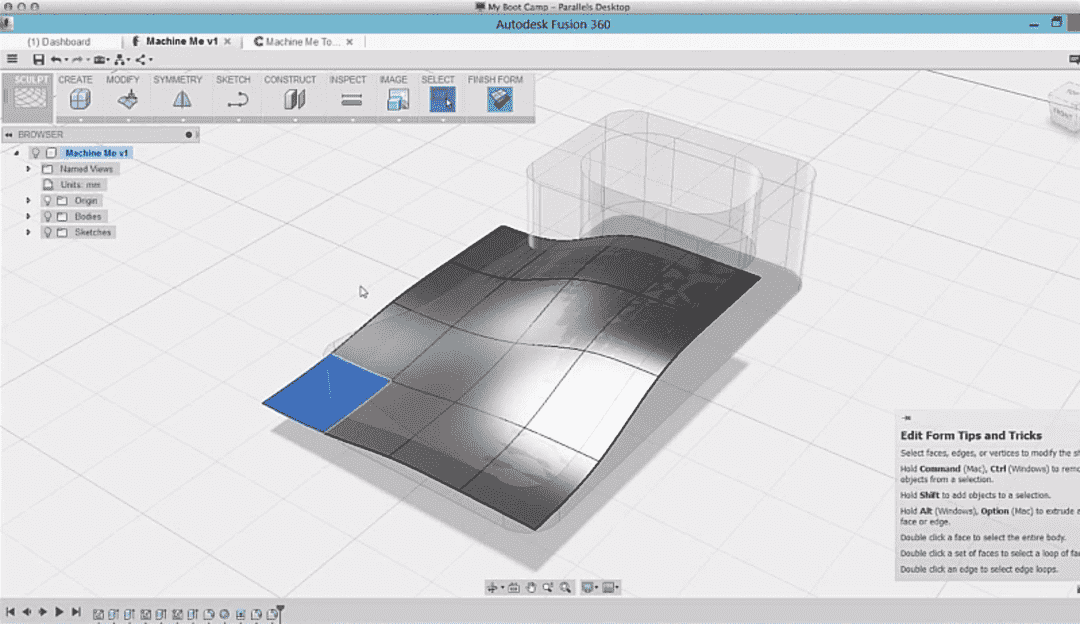
Autodesk's Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D design and manufacturing tool that offers a comprehensive set of features and tools to cater to every designer's needs. Parametric modeling, collaborative tools, simulation, rendering, and CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) tools are just a few of its cutting-edge capabilities. Additionally, Fusion 360 provides an intuitive user interface that streamlines 3D modeling while boosting productivity.
- Sketching
- Direct modeling
- Surface modeling
- Parametric modeling
- Mesh modeling
- Solid modeling
- Free form modeling
- Fusion 360 is a comprehensive design and engineering tool that offers a wide range of functionalities
- Being a cloud-based software, it allows for collaborative work and easy access from multiple devices
- It includes a set of tools that cater to 3D printing and additive manufacturing needs
- The software receives regular updates and new features to improve user experience
- The software requires a constant internet connection and has limited offline access
- Fusion 360 has a steep learning curve, which may be challenging for beginners
- The software might require high-performance hardware specifications to run smoothly
Pricing
- It costs $56.95 per month
2. Autodesk AutoCAD
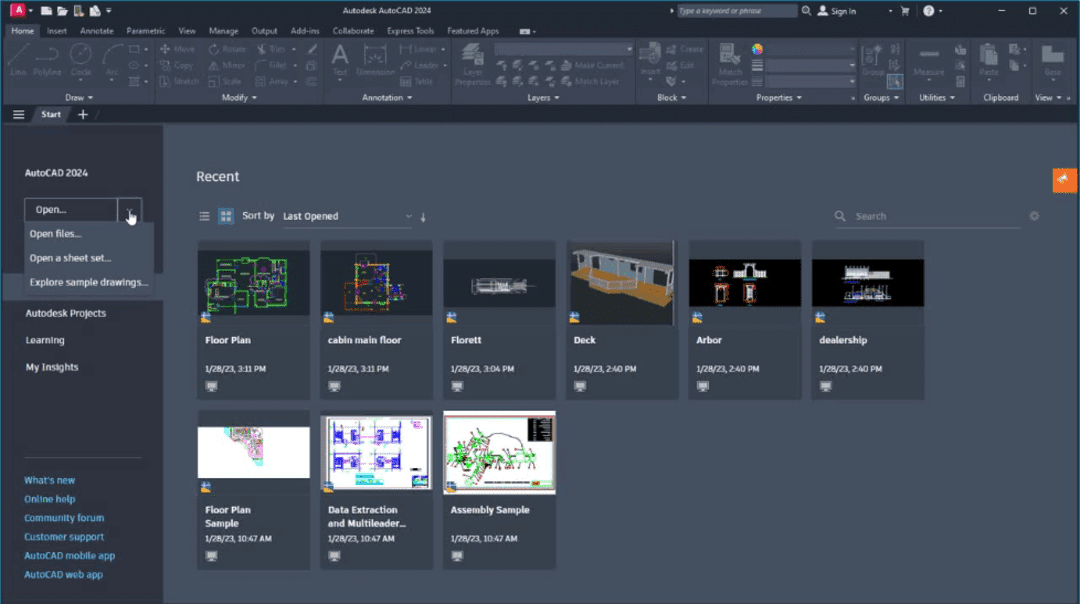
Autodesk's AutoCAD software has a range of features that make it a well-known choice for architects, engineers, and designers. The ability to create 2D or 3D graphics as well as import and export a range of file types are some of its standout features. Utilize cloud-based storage to work with team members in real-time as well. Additionally, it offers customized interface options as well as sophisticated capabilities for annotation, measurement, and customization.
- Smart blocks
- Activity insights
- Push to Autodesk docs
- Markup import and markup assist
- Floating windows
- AutoCAD is a feature-rich tool catering to diverse industry needs, from 2D and 3D drafting to modeling, annotation, and visualization.
- Despite its complexity, AutoCAD offers a user-friendly interface with intuitive commands, facilitating quick learning for beginners
- Collaborative capabilities allow multiple users to work together on projects, ideal for remote teams sharing files and working in real-time
- AutoCAD's customization options enable users to tailor the software with personalized tool palettes, keyboard shortcuts, and menus, enhancing workflow efficiency
- The cost of AutoCAD may be prohibitive for small businesses and individuals, limiting access to its capabilities
- Learning AutoCAD may require significant time and effort due to its complexity, possibly necessitating training or assistance
- Effective operation of AutoCAD demands powerful hardware, potentially incurring additional expenses for users to upgrade or acquire suitable computers
Pricing
- The platform costs $187.91 per month
3. Rhinoceros 3D
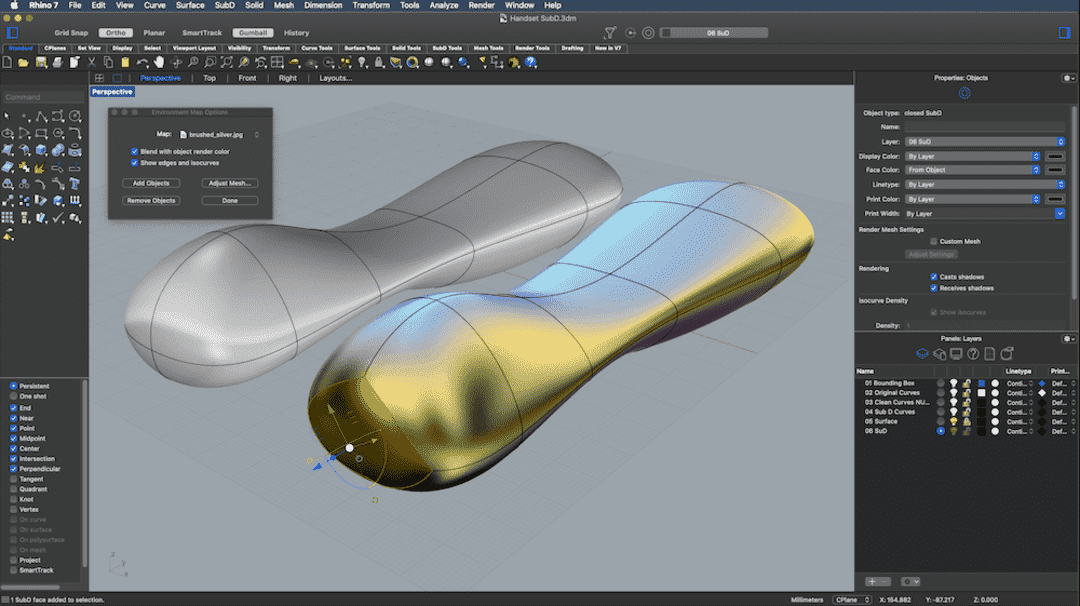
Rhino 3D stands as an advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software, empowering designers, engineers, and architects to craft impressive 3D models for diverse applications. Its user-friendly interface, powerful features, and unmatched versatility have earned it a prominent position among professionals in various fields. The software boasts an array of tools, including mesh editing, curve creation, and surface modeling, ensuring precision and creativity in every project.
- Rendering and presentation
- Drafting
- Digital fabrication
- Mesh tools
- 3D capture
- Inspection and analysis
- Rhino 3D can handle a wide range of design tasks, from product and industrial design to architecture and jewelry design
- Rhino 3D has a simple interface that is easy to use for both beginners and advanced users. The software has a range of video tutorials and user forums to help users learn and improve their skills
- Rhino 3D offers high-accuracy modeling due to its advanced algorithms for constructing and rendering models
- Rhino 3D allows users to customize the software to fit their preferences, where users can create custom toolbars or modify existing settings to enhance their workflow and increase productivity
- Rhino 3D has basic rendering capabilities that fall short when compared to other 3D modeling software such as Autodesk 3ds Max or SketchUp
- Rhino 3D takes some time to learn, especially for those new to 3D modeling
- Rhino 3D is a pricey software and may not be affordable for freelancers or hobbyists
Pricing
- Commercial for Windows and Mac US$ 995
- Students/faculties for Windows and Mac US$ 195
- Schools for Windows and Mac US$ 975
4. SketchUp
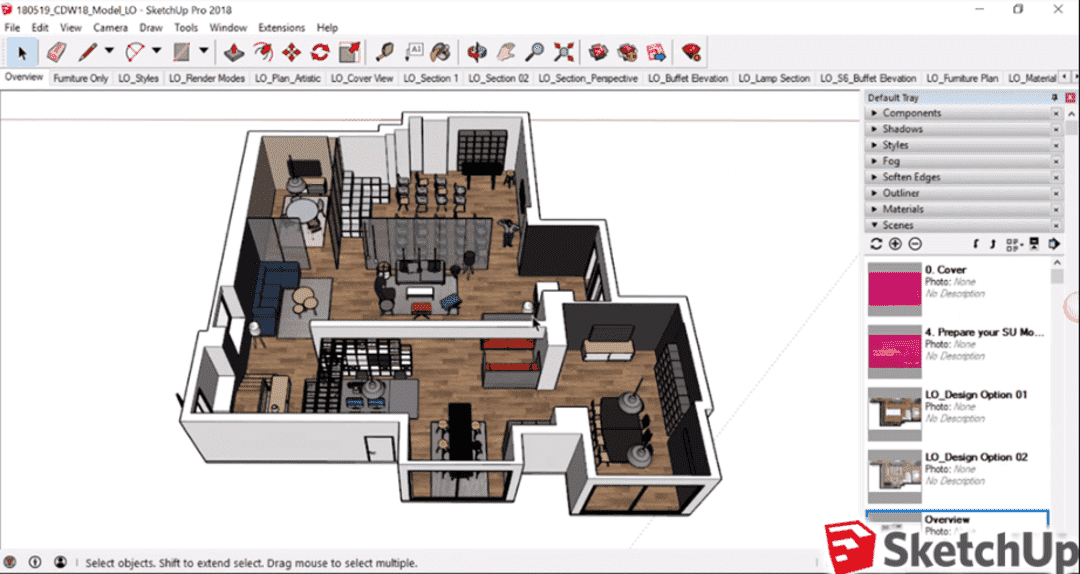
SketchUp, a 3D modeling program is utilized in a variety of fields, including engineering, interior design, and even video game development. SketchUp enables users to quickly generate and alter 3D models for their projects because of its user-friendly interface and robust features. The software is extremely adaptable and configurable thanks to its extensive library of pre-made models and plugins.
- Full-featured desktop modeler
- Create 2D documents and presentations
- 3D Warehouse
- VR model viewing
- Pre-made 3D models
- SketchUp has an intuitive interface and a shallow learning curve, making it easy for beginners to get started and create impressive designs quickly
- The platform has a wide range of modeling, rendering, and animation tools that make it possible to create highly detailed and complex designs
- The SketchUp community is vast, and users have created an extensive library of models and plugins that can be accessed and used at no cost
- Compared to other professional 3D modeling software, SketchUp is relatively affordable, making it accessible for freelancers and small establishments
- SketchUp's rendering capabilities are somewhat limited, and users often have to rely on external plugins or software to create high-quality renderings
- SketchUp is equipped with basic modeling tools but lacks some of the advanced features found in more professional software
- Files created in SketchUp can have compatibility issues with other software, requiring users to save files in different formats and adjust settings to make them compatible
Pricing
- Go- $119 per year
- Pro- $349 per year
- Studio- $749 per year
5. Creo
Creo is a 3D CAD system that enables you to design better things more quickly by accelerating product innovation. It is simple to use and takes you smoothly from the initial stages of product design to manufacturing and beyond. Creo blends cutting-edge technologies like generative design, real-time simulation, sophisticated manufacturing, IIoT, and augmented reality with strong, tried-and-true functionality.
- Generative design
- Legacy Data Migration
- Advanced manufacturing
- Augmented reality
- Ansys simulation
- Creo offers an extensive array of design and engineering tools, facilitating the creation of intricate parts and assemblies
- Its user-friendly interface caters to both beginners and experienced users, streamlining the process of crafting 3D designs
- With support for various file formats like STEP, IGES, and DWG, Creo simplifies importing and exporting designs from different CAD platforms
- Creo's customization options empower users to adapt the software to their specific design and engineering needs, enhancing flexibility and control
- Creo's higher cost compared to other CAD platforms may be impractical for small businesses and individual users
- While user-friendly, some individuals might find Creo initially overwhelming, necessitating additional training
- Due to its resource-intensive nature, Creo demands substantial processing power, which may not be feasible for certain users
Pricing
- Custom pricing.
What is The Setup Process of 3D Printing Software?

For setting up 3D printing software, few things must be ensured.
3D printing requires a balance between slicing settings and material properties. A designer must work with these constraints to be able to create a proper digital model. The following must be taken into consideration during the setup process:
First, to install and configure the software, a few series of steps must be followed.
The 3D file (STL, OBJ, or 3MF), exported from CAD 3D modeling software to 3D printing software (also called slicer), comes into the picture. In the printer settings, adjust the depth and width (increase it), for example, from 220mm to 235mm.
Then need to put it on the virtual print bed. The toolbox will open where the dimension can be increased or decreased, or the object can be rotated.
-
Geometry: While giving an FFF print, geometry becomes more crucial because geometrically complex parts need adhesion structures or support material. These additional materials can be created with the help of slicer software.
-
Slicing Setting: There are two common settings here.
-
Overhangs and Support: Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printing is a bottom-up process, which means each layer is supported by a layer underneath it. Support material is used if an object has an extended part.
-
Adhesion: This is an important part as it gives the 3D object the support it requires. The most used method is called a brim – it prints an additional border.
-
Thickness: The thickness of the wall must be specified before printing; one must keep in mind that the wall thickness of the object must be greater than the nozzle being used in the printing process.
-
Layer Height: The thickness of each layer is known as layer height. Thicker layer height will reduce the resolution and the print time, whereas the thinner layer produces sharper resolution but extends the printing time.
What are The Latest Trends of 3D Printing Software?

-
Software Interoperability
As we move toward a faster and easier design preparation workflow, we need greater software integration. Interoperability helps reduce the number of tools and steps and efforts needed in designing a model. Now, this is happening in multiple ways such as software integration, acquisition, or development of capabilities internally.
-
Replacing STL files
STL files were invented in the mid-1980s, which enabled CAD software to transit files to prints 3D objects. These STL files are a little difficult to use because they have many limitations such as unable to accurately define large and complex geometric shapes. The format does not specify color, texture, and many others. Hence, the introduction of 3MF, an open-source 3D file format, was quite a relief for users.
-
Focus on Workflow Software
Workflow management software has witnessed tremendous growth and helps overcome workflow inefficiencies.
-
Growth of Simulation Software
It is an excellent choice for minimizing the print failures that happen in later stages. It is used at the design stage to digitally reproduce how a material would behave during the printing process.
-
Combining the Software with AI
This integration would further enhance the design and workflow process on the design front itself. AI gives engineers the option to explore unexpected design options.
-
Increased Productivity
The software helps in automating the entire process, streamlining the whole process, and reducing labor costs. Hence it will be easier to maintain track of productivity.
-
Wide Usage in the Medical Industry
It will be a huge revolution in the medical industry as it is now capable of creating fully functional human organs.
Research Report of 3D Printing Software
The research report on the 3D printing software market talks about a market overview and an in-depth study of how the market will grow in the near future. The 3D printing market is also segmented based on its offering, process, application, end-user, and geographical location.
A complete SWOT analysis of the 3D printing market is done to understand its growth factors, restraints, opportunities, and challenges. The market is strategically analyzed, depending on its market trends and recent development in 3D printing. With the identification of newer opportunities in the market, companies can enhance their strategies and products to gain a competitive advantage. Also, the good impact of 3d printing software on supply areas.The entire 3D printing market is studied, covering demand and supply areas.
The supply side of the 3D printing market covers the market based on its offering, process, technology, and application. Offering includes a printer, material, software, and service. The process covers powder bed fusion, material extrusion, material jetting, binder jetting, sheet lamination, etc. Technology includes stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, selective laser sintering, inkjet printing, direct metal laser sintering, and multijet printing. The application includes prototyping, functional part manufacturing, and tooling. The demand side is analyzed based on end-users and regions. Various end-users comprise industrial, healthcare, consumer, automotive, education, jewelry, food, and many more. Geographical regions cover North America, Europe, APAC, and RoW.
The research report on 3D printing software includes a competitive landscape that briefly summarizes the leading players in the 3D printing market. All the growth strategies of the organization are discussed in this part. The strategies are divided into Organic and Inorganic strategies, wherein organic covers product launches/developments and expansions, inorganic covers mergers/acquisitions, and partnerships/agreements/collaborations. In this section, companies are rated based on their technological expertise, product offering, market share contribution, target market, and mergers & acquisitions.
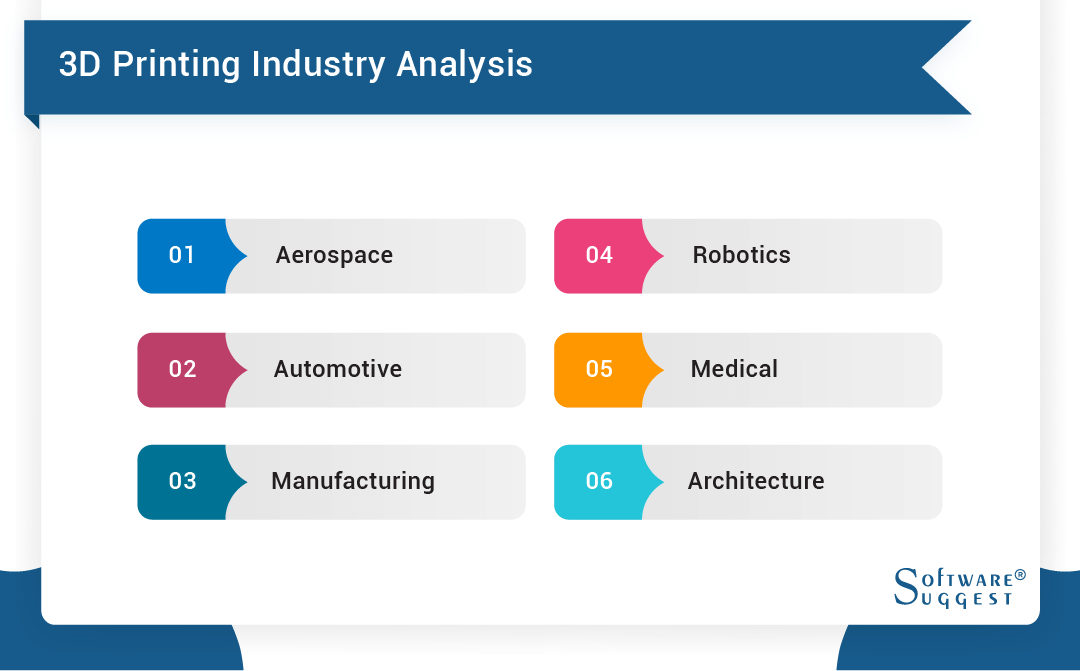
3D Printing Industry Analysis
The global 3D printing market size was valued at USD 13.78 billion in 2020 is expected to grow at the rate of CAGR of 21%. Following are the industries where 3D printing is widely used:
-
Aerospace: This industry expects the highest standards in part performance. The parts must be able to withstand high temperature and chemical resistance. Part failure often results in system failure, which is not an option.
-
Automotive: This is one industry that has been ahead in using additive manufacturing. For example, Audi has been using 3D printing for many years. The most common printed parts by automotive manufactures are cradles, fixtures, and prototypes, which are supposed to be stiff and durable.
-
Manufacturing: 3D printing is giving the manufacturing industry an opportunity to create customized low-volume tooling and fixtures at the traditional price.
-
Robotics: 3D printing is useful for making parts like grippers and sensor mounts, which are expensive to fabricate.
-
Medical: This industry has been using 3D printing in several ways possible for many years. For example, dentists use 3D scanners to get a 3D print of their patient’s jaw. Dentists produce 3D printed braces, aligners, dentures, and other things as well. Doctors and engineers had also developed knee replacements.
-
Architecture: From preparing a 3D model to an actual house, 3D printing is extremely useful for this industry. It gives architects a better opportunity to make their clients understand the space they are about to purchase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of 3D printing platforms presents an extensive range of options, each tailored to diverse user needs and skill levels. Throughout our comprehensive buyer guide, we have delved into some of the finest 3D printing software available, meticulously considering vital factors such as functionality, user-friendliness, versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
Ultimately, the ideal 3D printing software choice hinges upon individual requirements and specific user goals. By diligently assessing the features and capabilities of each software, users gain the confidence to handpick the most suitable option for their unique projects. Therefore, unleashing their creativity and pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with 3D printing technology.
The advancing 3D printing technology encourages exploration and experimentation. It leads to groundbreaking innovations and remarkable creations, elevating its potential. This cutting-edge technology propels us into a new era of manufacturing and design.
FAQs
Anything with a digital component requires programming. But on the one hand, you need programming to implement 3D graphics in the software and program the printer itself. But programming skills are not required to use and operate 3D printing software.
The 3D printer software is available starting from $500 to $15,000, depending on multiple factors. The scale of your project also affects the price of your software. There are many free, open-source software identical available, but there is a lack of professional support, object libraries, and support for multiple printers or materials.






















